GXB - Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
- Home
- Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
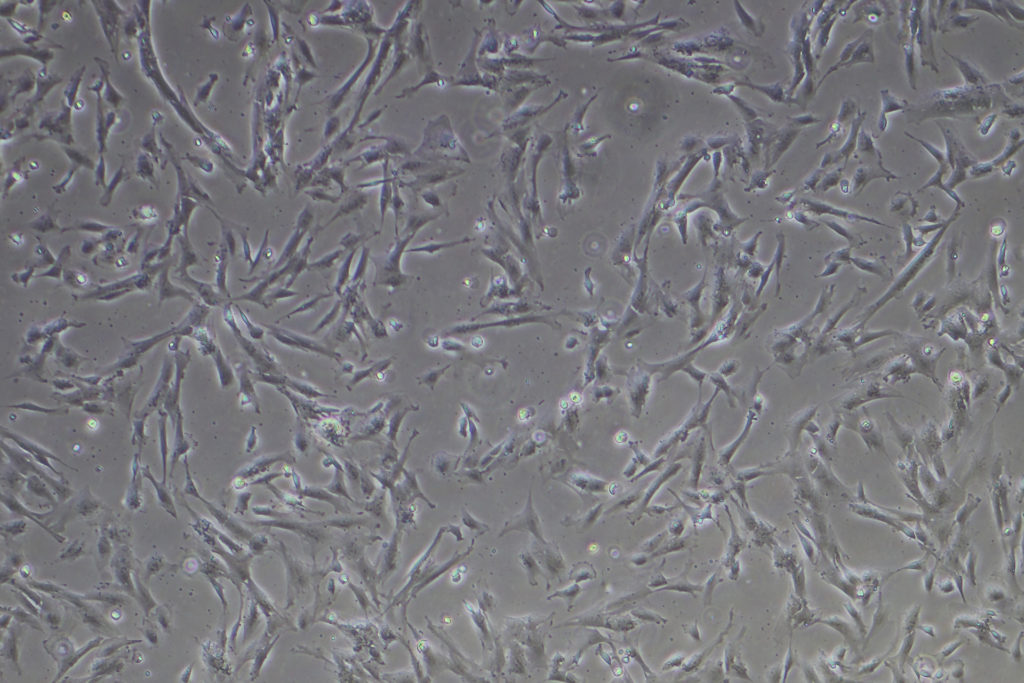
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a type of adult stem cell that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including bone cells, cartilage cells, and fat cells. They are found in various tissues in the body, including bone marrow, fat, and muscle, and have the ability to self-renew, or produce more MSCs.
MSCs have several potential therapeutic uses due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types and their ability to modulate immune responses. They have been studied for use in a variety of conditions, including osteoarthritis, cardiovascular disease, and various inflammatory conditions.
There is ongoing research into the use of MSCs for cell-based therapies, and MSCs have shown promise in early clinical trials for a range of indications.
There are several sources of stem cells, including:
Embryonic stem cells: These are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst (a structure that forms during the early stages of embryonic development) and have the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body.
Adult stem cells: These are found in various tissues throughout the body and have the ability to differentiate into a limited number of cell types. Examples include hematopoietic stem cells (found in bone marrow and responsible for producing blood cells), mesenchymal stem cells (found in bone marrow, fat, and muscle and able to differentiate into bone cells, cartilage cells, and fat cells), and neural stem cells (found in the brain and able to differentiate into neurons and glial cells).
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs): These are adult cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell-like state and have the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body.
Umbilical cord blood stem cells: These are found in the blood remaining in the placenta and the umbilical cord after birth and have the ability to differentiate into various blood cells.
Stem cells have the potential to be used in a variety of medical applications, including tissue repair and regeneration, and are the subject of much scientific research and clinical trials.
GXB AVAILABLE MSC SOURCES
Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells:
UC-MSCs
Amniotic Membrane Mesenchymal Stem Cells:
AM-MSCs
Induced Mesenchymal Stem Cells:
i-MSCs
Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cells:
A-MSCs
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells:
BM-MSCs
