GXB - Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
- Home
- Stem Cells
Stem Cells
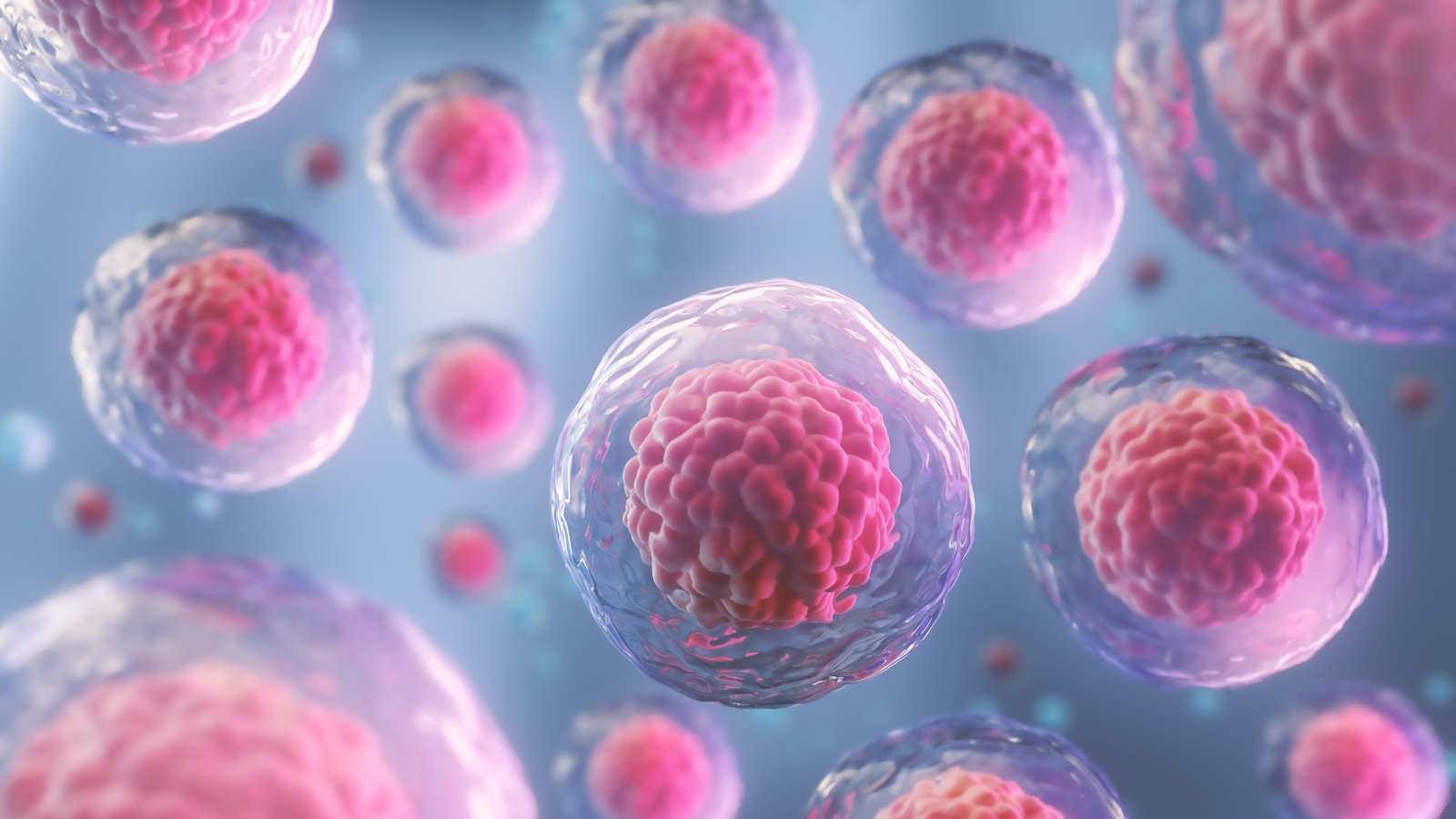
Stem cells are special types of cells that have the ability to self-renew, or produce more stem cells, and to differentiate into various cell types in the body. There are two main types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells.
Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, a structure that forms during the early stages of embryonic development. They have the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body and are considered to be pluripotent.
Stem cells have the potential to be used in a variety of medical applications, including tissue repair and regeneration, and are the subject of much scientific research and clinical trials.
PLURIPOTENT
Pluripotent stem cells are a type of stem cell that has the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body.
MULTI-POTENT
Multipotent stem cells are a type of stem cell that has the ability to differentiate into a limited number of cell types. They are found in various tissues throughout the body and are responsible for maintaining and repairing those tissues.
PROGENITOR
Progenitor cells, also known as precursors or committed cells, are cells that have the ability to differentiate into a specific cell type, but have limited capacity for self-renewal.
