GXB - Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
- Home
- Immune Cells
Immune Cells
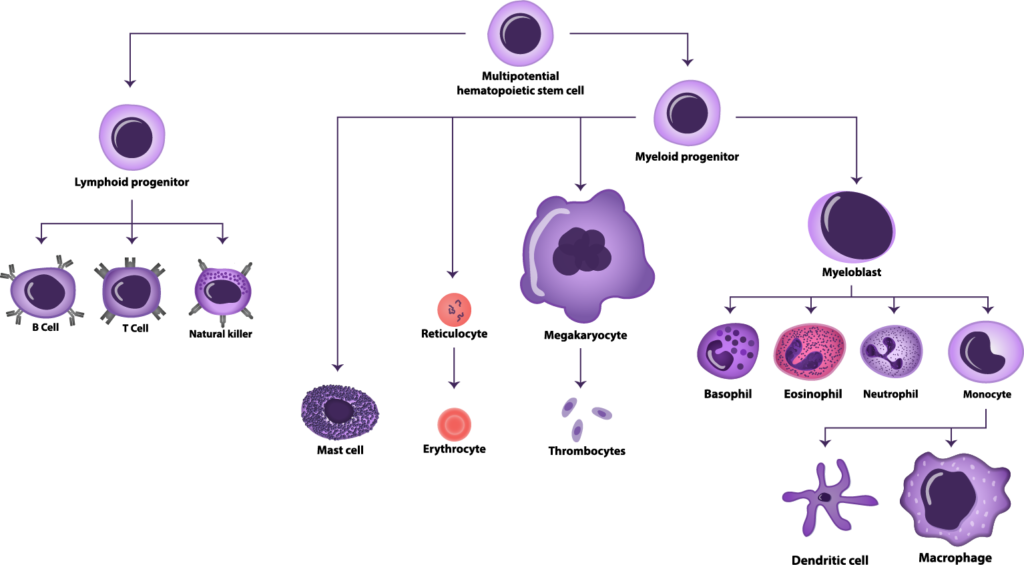
Immune cells, also known as leukocytes or white blood cells, are a type of blood cell that plays a crucial role in the body’s immune system. They are responsible for protecting the body against infection and disease by identifying and eliminating harmful substances, such as bacteria and viruses.
There are several types of immune cells, including:
T cells: T cells, also known as T lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell that plays a central role in the body’s immune response. There are several subtypes of T cells, including CD4+ T cells (also known as helper T cells), CD8+ T cells (also known as killer T cells), and regulatory T cells.
B cells: B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to help fight infection and disease.
Natural killer (NK) cells: NK cells are a type of immune cell that can recognize and eliminate infected or cancerous cells.
Macrophages: Macrophages are a type of immune cell that can engulf and destroy foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses.
Neutrophils: Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that can recognize and eliminate bacteria and other foreign substances.
Immune cells are essential for maintaining the body’s overall health and well-being, and they play a key role in the body’s ability to fight infection and disease.