GXB - Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
- Home
- Natural Killer Cells (NK Cells)
Natural Killer Cells (NK Cells)
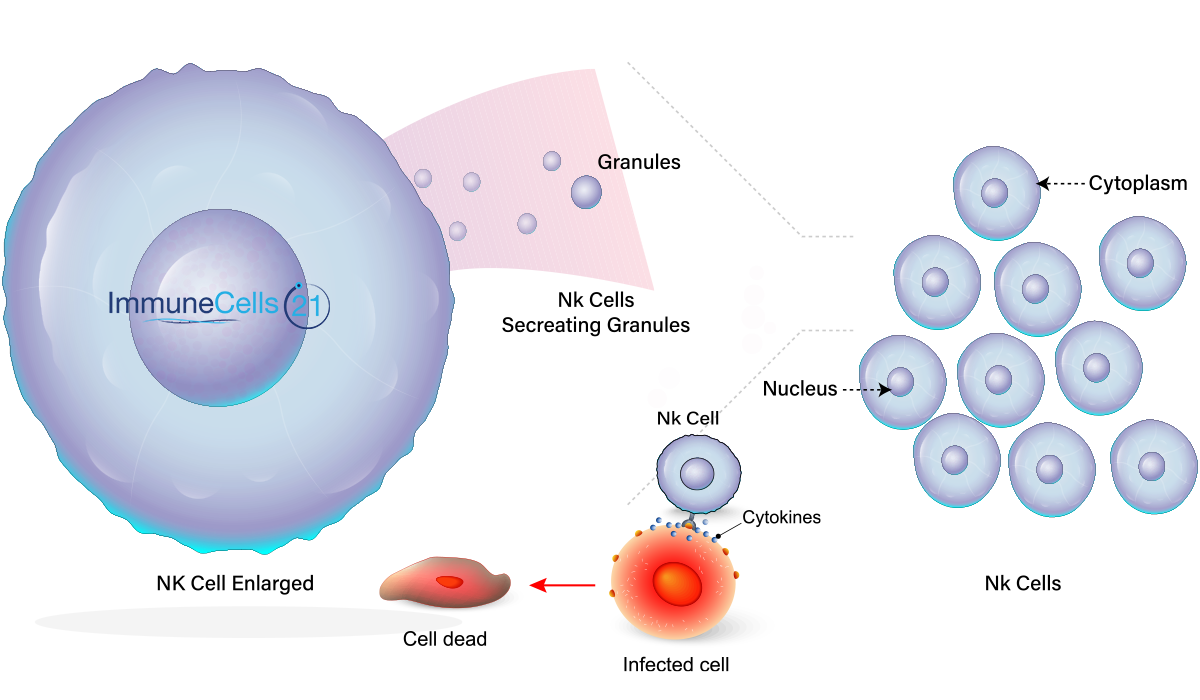
Natural killer (NK) cells are a type of immune cell that plays a crucial role in the body's immune system. They are responsible for recognizing and eliminating infected or cancerous cells, and are an important part of the body's first line of defense against infection and disease.
NK cells have the ability to recognize and attack cells that are infected with viruses or that have become cancerous, as well as cells that are undergoing abnormal changes, such as those that occur during the early stages of cancer development. They do this by releasing substances called cytotoxins, which can kill infected or cancerous cells.
NK cells are also involved in the regulation of the immune system and can help to suppress the activity of other immune cells. This helps to prevent overactive immune responses, which can lead to autoimmune diseases.
NK cells are an important part of the body's immune system and play a key role in the body's ability to fight infection and disease. They are also the subject of much scientific research, with ongoing studies focusing on their potential use in the treatment of cancer and other immune-related conditions.